The Department of Health today reported that a young child and a young adult are recovering after being diagnosed with meningococcal disease. The cases are not linked, and were infected with different types (B and W) of the organism.
Meningococcal disease is an uncommon, life-threatening illness caused by a bacterial infection of the blood and/or the membranes that line the spinal cord and brain, and occasionally of other sites, such as the throat, lungs or large joints.
There have been nineteen cases reported to date in 2018, comprising thirteen serogroup W, four serogroup B and two serogroup Y meningococcal infections.
A total of 46 cases were notified in WA in 2017, double the number reported in 2016 and the most in any year since 2005. The 46 cases comprised 23 serogroup W, 9 serogroup Y, 12 serogroup B, and one serogroup C infection, along with a case in whom the type could not be determined. The numbers of serogroup W and Y cases in 2017 were well above the long term average of less than one case per year of each of these types, and the most ever recorded in WA.
The incidence of meningococcal disease had previously decreased significantly in WA – down from a peak of 86 cases in 2000 to a low of 16 cases in 2013 – but is now increasing again due to the emergence of new virulent strains of serogroup W, and to a lesser extent serogroup Y, meningococcal bacteria.
The Department of Health routinely identifies the close contacts of all notified cases of meningococcal disease and provides them with information and, where appropriate, antibiotics and a vaccine. This is to minimise the chance of further spread of the organism to others, should one or more of the contacts be carrying the strain that caused disease.
Meningococcal bacteria are carried harmlessly in the back of the nose and throat by about 10-20 per cent of the population at any one time. Very rarely, the bacteria invade the bloodstream or tissues and cause serious infections.
Meningococcal bacteria are not easily spread from person-to-person. The bacterium is present in droplets discharged from the nose and throat when coughing or sneezing, but is not spread by saliva and does not survive more than a few seconds in the environment.
Invasive meningococcal infection is most common in babies and young children, and older teenagers and young adults, but infection can occur at any age. Serogroup W and Y infections are associated with a third age peak in adults over 60 years.
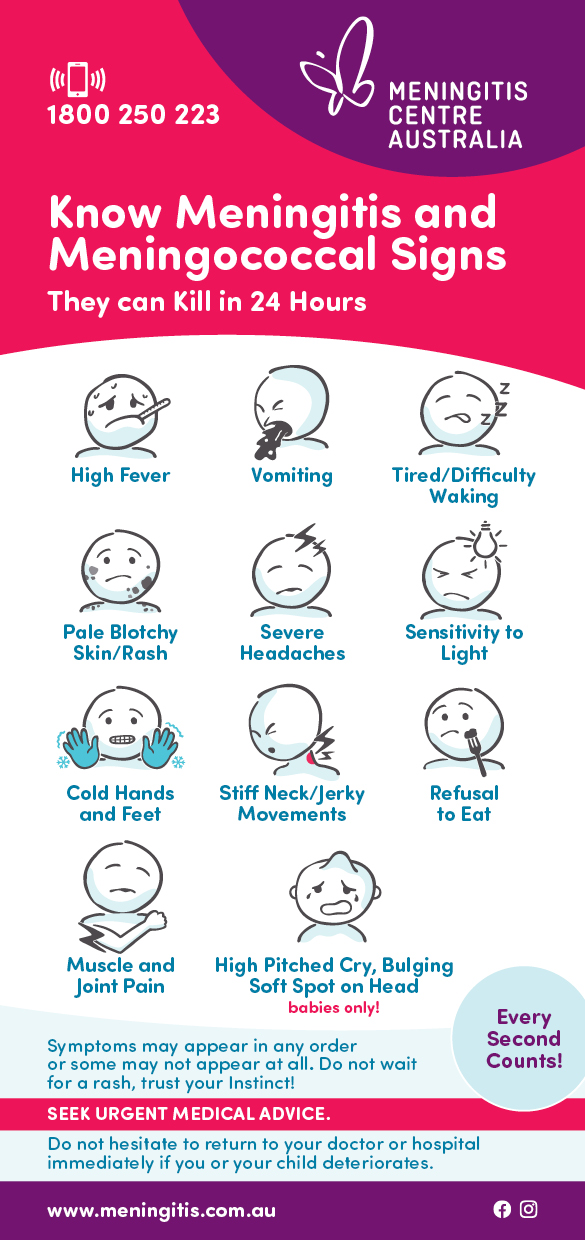
Symptoms may include high fever, chills, headache, neck stiffness, nausea and vomiting, drowsiness, confusion, and severe muscle and joint pains. Young children may not complain of symptoms, so fever, pale or blotchy complexion, vomiting, lethargy (blank staring, floppiness, inactivity, being hard to wake, or poor feeding) and rash are important signs.
Sometimes – but not always – symptoms may be accompanied by the appearance of a spotty red-purple rash that looks like small bleeding points beneath the skin or bruises.
Although treatable with antibiotics, meningococcal infection can progress very rapidly, so it is important that anyone experiencing these symptoms seeks medical attention promptly. With appropriate treatment, most people with the disease recover, although around 5 to 10 per cent will die and around 15 per cent may experience complications such as hearing loss, or gangrene requiring skin grafts or amputations.
A vaccine to protect against the serogroup C type of meningococcal disease, which is now very rare, continues to be provided free to children at 12 months of age. A vaccine against serogroup B meningococcal infection, historically the most common type in WA, is available on prescription. Combination vaccines that protect against four serogroups of the organism (serogroups A, W and Y, in addition to serogroup C) are also available on prescription, or are provided free for young children and adolescents, as detailed below.
As a result of the increase in serogroup W and Y disease in WA over the past three years, a funded state-wide meningococcal ACWY vaccination program for adolescents aged 15 to 19 years commenced in 2017. In 2018 and 2019, the program is targeting incoming Year 10 students in schools, while other individuals aged 15-19 years can currently continue to access free catch-up vaccination through other immunisation providers.
The state-funded meningococcal ACWY vaccine program was expanded to include children aged 1-4 years in January this year, and vaccines for young children are currently available from GPs and other childhood immunisation providers.
Details of the 12 months to 4 years and adolescent (15-19 years) meningococcal ACWY vaccine program, including where to access the free vaccine, are available at: http://healthywa.wa.gov.au/Articles/J_M/Meningococcal-vaccine
SOURCE: WA Health Department